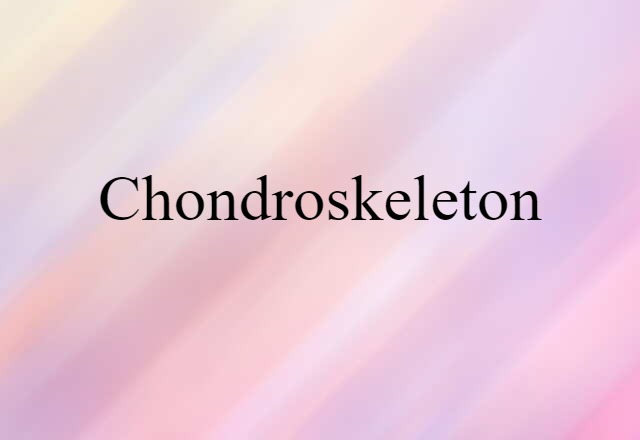- a 15th-century compositional technique employing three voices, the upper and lower voices progressing an octave or a sixth apart while the middle voice extemporaneously doubles the upper part at a fourth below.
- the use of progressions of parallel sixth chords.